What is the Difference Between Isotype Allotype and Idiotype
In immunology, the terms isotype, allotype, and idiotype are used to describe distinct characteristics of an antibody or immunoglobulin (Ig). Each term has a unique definition and refers to specific features of an antibody’s structure or function. This article will explore and contrast the differences between these three terms, presenting information in an objective and informational tone.
Here is a table that summarizes the differences between isotype, allotype, and idiotype:
| Feature | Isotype | Allotype | Idiotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Constant region of heavy chain and light chain | Constant region of heavy chain | Variable region of heavy chain and light chain |
| Function | Structural | Structural | Functional |
| Inheritance | Inherited | Inherited | Not inherited |
| Antigenic determinant | Determined by amino acid sequence | Determined by amino acid sequence | Determined by amino acid sequence and conformation |
| Use | Identify class and subclass of antibodies | Identify different clones of B cells | Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases |
What is idiotype immunology?
Idiotype are antigenic determinants which refers to the class or subclass of an immunoglobulin, determined by the structure and amino acid sequence of the constant regions of the heavy and light chains.

It reflects the maturation stage of B cells. Naïve B cells express the antibody isotypes IgM and IgD with unmutated variable genes. There are five main classes of immunoglobulins in humans, commonly known as IgA, IgG, IgM, IgE, and IgD. These classes have distinct roles in the immune response and some inherent functional differences, such as the ability to fix complement or cross the placenta.
Key Points about Isotype:
- Refers to the class or subclass of an immunoglobulin
- Defined by the structure and amino acid sequences of the constant regions of the antibody
- There are 5 main classes.
Types of Isotypes
There are five main types of isotypes: IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD. Each of these Antigenic determinants serves a different function within the immune system.
Characteristics of Each Isotype
Each isotype has unique characteristics that set it apart from the others. For example, IgG is the most common Immunoglobulins in the body. Its responsible for long-term immunity and IgM is the first antibody to be produced by the body in response to any infection.
Structure
The structure of each isotype varies slightly, but all antibodies have a Y-shaped structure composed of four polypeptide chains.
Function
The function of each Immunoglobulins also varies, depending on the specific antibody. However, all antibodies work to recognize and neutralize foreign molecules within the body.
Role of Isotype in Disease
Isotypes can lead to a variety of diseases and conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or immunodeficiency disorders.
What is Allotype
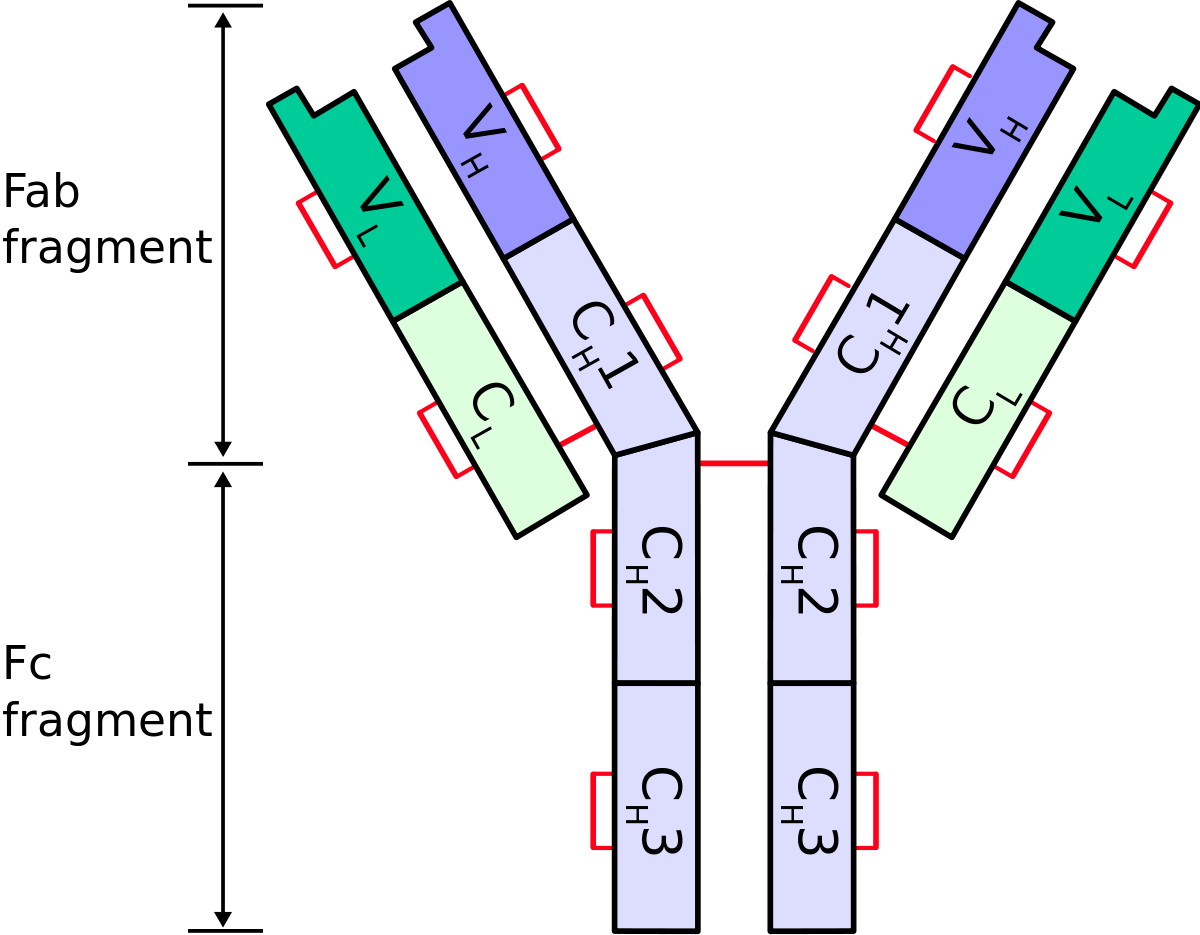
An allotype is a genetic variant of an immunoglobulin molecule found within a population. Allotypes result from slight differences in the amino acid sequence of the heavy and light chains, primarily within the constant region, due to allelic variation. These differences do not alter the antibody’s overall function; however, they can play a role in individual responses to infection or vaccination.
Key Points about Allotype:
- Genetic variation of an immunoglobulin within a population
- Results from differences in the amino acid sequence of the constant regions of the heavy and light chains
- Does not significantly change the antibody’s function but may affect individual responses
Types of Allotypes
There are three main types of allotypes: alpha, gamma, and kappa. Each of these types is characterize by specific genetic variations.

Process of Allotype Inheritance
Allotypes are inherited from generation to next through the genes of the parent.
Uses of Allotype in Research
Allotypes use in research to study the genetic diversity of different populations and to identify individuals who may be at higher risk for certain diseases.
What is Idiotype
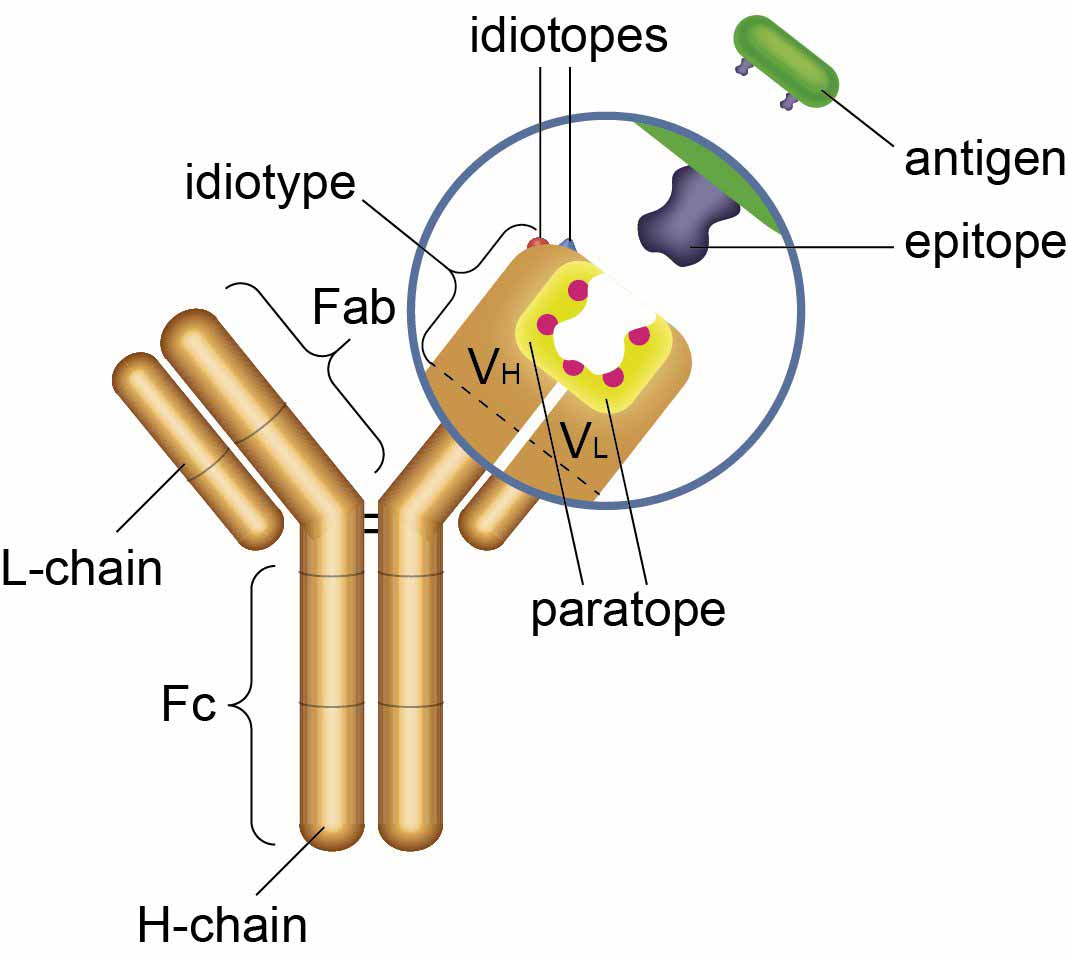
An idiotype is the unique antigenic determinant (epitope) present on an antibody, created by combining the variable regions of the heavy and light chains. It determines the specificity of the antibody, in other words, the antigen it will bind to. Since each individual generates a vast and diverse repertoire of antibodies, each with a unique Antigenic determinants, the antibody specificity can vary greatly between individuals.
Key Points:
- Unique antigenic determinant (epitope) on an antibody
- Defined by the variable regions of the heavy and light chains
- Determines the antibody’s specificity and antigen-binding capacity
Types of Idiotypes
There are two main types of idiotypes: private and public Variable region. Private idiotypes are unique to each individual, while public idiotypes are share among individuals with similar genetic backgrounds.
Unique Structure and Location
The unique structure and location of the Variable region make it a useful tool for identifying and characterizing different antibodies.
Function of Idiotype in Immune Response
It plays an important role in the immune response by allowing the body to recognize and response at foreign molecules.
What is the Difference Between Isotype Allotype and Idiotype?
Comparison and Key Takeaways
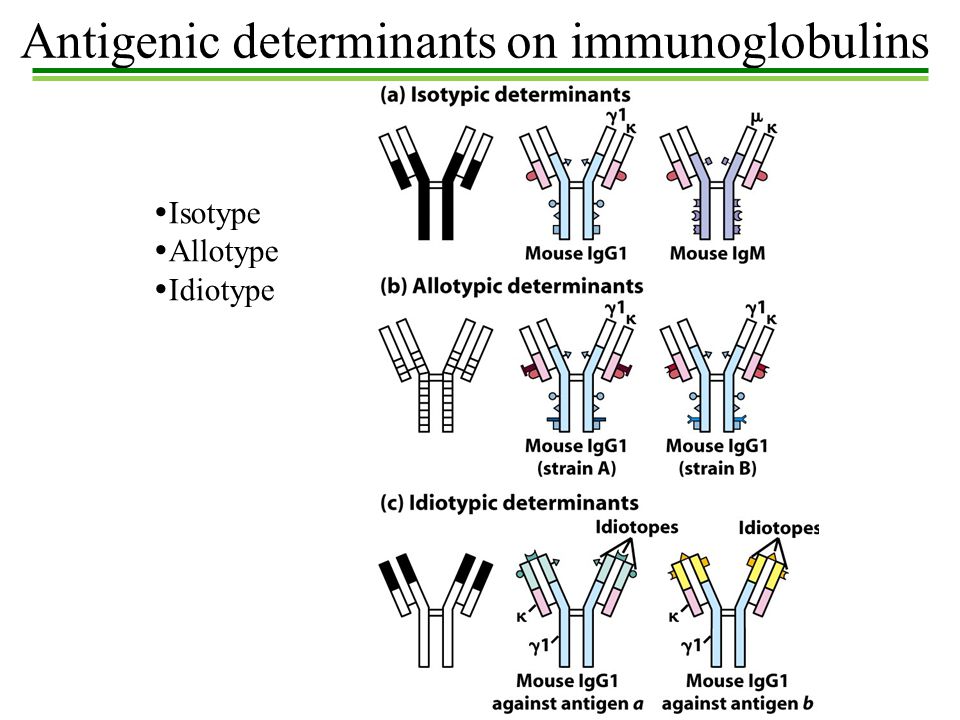
In summary, isotype, allotype, and idiotype are categories of antigenic determinants present in immunoglobulin molecules.
- Isotypes are determined by constant regions of heavy and light chains, grouping antibodies by their function in immune responses.
- Allotypes are genetically inherited variations within constant regions, providing a basis for genetic, population, and paternity studies.
- Idiotypes are unique antigenic determinants present in the variable regions of an antibody, defining its antigen specificity.
Comparison: Isotype vs. Allotype vs. Idiotype:
- Isotype, allotype, and idiotype are distinct antigenic determinants in the realm of antibodies.
- Isotype refers to the classification of antibodies into different classes based on heavy chains and types and subtypes, while allotype denotes genetic variations in antibodies, and idiotype represents unique antigenic determinants in the variable region.
- Isotypes are classified by immunoglobulin classes, allotypes vary between individuals, and idiotypes are unique to specific antibodies.
- Its crucial for unraveling the complexity of the immune system and developing targeted therapies.
Read Related Post What Is the Difference Between Thrombus and Embolism?
What are the Similarities Between Isotype Allotype and Idiotype?
- Antigenic determinants: All three are specific features of antibodies that contribute to their recognition and binding capabilities.
- Related to the immune system: They are all involved in the immune response and antibody variability.
- Different regions of an antibody: They are present in distinct regions of an antibody molecule.
- Induce immune responses: They can trigger immune reactions when needed.
What is anti-idiotype antibody?
An anti-idiotype antibody is an antibody that specifically targets and binds to the unique characteristics of another antibody’s variable region. Each antibody has only one type of (γ, or α, or μ, or ε, or δ) heavy chain and one type of (k or λ) light chain. It can be use in research and therapeutics to mimic or block the binding of the original antibody.
Anti-idiotype antibodies can be use for a variety of purposes, including:
- Diagnosing and monitoring autoimmune diseases. Anti-idiotype antibodies can be use to detect autoantibodies, which are antibodies that attack the body’s own tissues.
- Treating cancer. They antibodies can be use to target cancer cells.
- Developing new vaccines. They antibodies can be use to develop new vaccines.
Summary – Isotype vs Allotype vs Idiotype
In summary, while the isotype refers to the antibody’s class or subclass, the allotype describes the minor genetic variations that occur within a population, and the idiotype defines the unique antigen-binding specificity of an antibody. Understanding these differences is essential for studying and manipulating the immune response in various medical and research settings.
Refence Links



