Difference Between Gooch Crucible and Sintered Glass Crucible
When it comes to laboratory equipment, crucibles play a crucial role in various scientific processes. Crucibles are vessels use in chemistry labs and industrial settings to withstand extremely high temperatures.
They have a variety of applications including melting metals, calcining powders, fusing glass, and firing ceramics.
The most common types of crucibles are Gooch crucibles and sintered glass crucibles. While both have their advantages and limitations, sintered glass crucibles are generally preferred for most uses.
The following table summarizes the key distinctions between Gooch crucibles and sintered glass crucibles:
| Aspect | Gooch Crucible | Sintered Glass Crucible |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Porcelain | Pyrex Glass |
| Filtration Utility | Collects precipitates within the vessel | Directly collects precipitates requiring drying |
| Temperature Resistance | Withstands high temperatures | Limited resistance, up to 400°C |
| Material Used | Porcelain | Pyrex Glass |
| Important Applications | Gravimetric analysis, ashing | Precipitate drying |
What is a Crucible?

A crucible is a container made from materials capable of withstanding high melting points and thermal shock. Desired properties include:
- High melting point
- Resistance to thermal shock
- Chemical inertness
Crucibles allow scientists and engineers to work with substances at temperatures above 1000°C safely. Common crucible uses are melting points, gravimetric analysis, flux preparations, and high temperature ignitions.
Gooch Crucibles
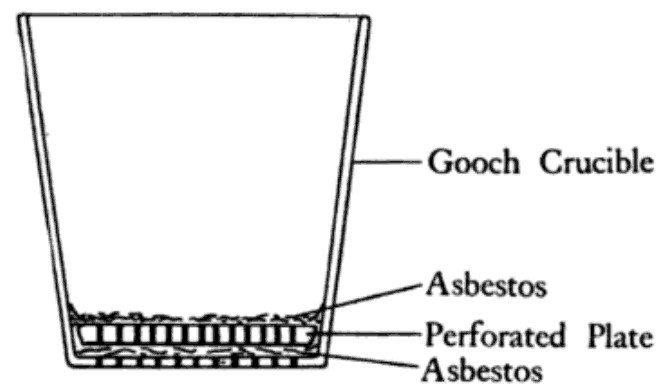
Gooch crucibles are porous ceramic vessels usually made from alumina or porcelain. They have a perforated bottom attached to a stem made of the same porous material.
A Gooch crucible is a small porcelain or glass funnel containing a perforated bottom plate and integrated glass fiber mat.
The perforated bottom allows liquid to pass through while the glass fibers trap solid materials. This serves as an alternative to sintered glass for filtration applications.
Gooch crucibles provide fast filtration rates due to the large surface area of the glass fibers. They can also withstand high temperatures.
However, the glass fibers are more prone to blocking compared to sintered glass. Gooch crucibles are not reusable and the glass fibers may shed, contaminating the filtered solids.
Key features of Gooch crucibles include:
- Porous texture enables filtration directly inside
- Relatively inexpensive
- Limited temperature range up to 1000°C
- Prone to breakage due to thermal shock
- Not reusable
- Can absorb samples and contaminants
Gooch crucibles are ideal for gravimetric analysis and filtrations at lower temperatures. However, their porous and fragile nature makes them unsuitable for reuse or applications above 1000°C.
Pros:
- Inexpensive
- Allow direct filtration
- Widely available
Cons:
- Limited temperature range
- Fragile, prone to breakage
- Porous, absorbs samples
- Not reusable
Sintered Glass Crucibles
Sintered glass crucibles are made by fusing pure quartz glass (SiO2) particles into a solid, non-porous structure.

The resulting glass contains many small interconnected pores, giving it a spongy texture. Sintered glass discs or frits are commonly used as filtration media, particularly for gravity filtration.
The pore size of sintered glass can be controlled during manufacture, with typical pore sizes ranging from 10-100 microns. This allows size selectivity during filtration.
The pores also provide a high surface area for filtration. Sintered glass is chemically durable and can withstand high temperatures and pressures. It is commonly used to filter precipitates, gelatinous materials, and corrosive chemicals that would degrade paper filters.
Key properties of sintered glass crucibles:
- Non-porous, impermeable surface
- Withstand temperatures up to 1600°C
- Excellent chemical resistance and inertness
- Reusable many times
- Easy to clean
- More expensive than Gooch crucibles
- Cannot be used for filtrations
The impervious structure and durability of sintered glass makes them ideal for high temperature inorganic fusions and repeated use. However, their non-porous nature prevents direct filtration.
Pros:
- Withstands very high temps
- Chemically durable and inert
- Reusable many times
- Easy to clean
Cons:
- More expensive
- Cannot filter solutions
- Requires careful handling
Read more about What is difference Between Incineration and Pyrolysis in Waste Management
Differences Between Gooch Crucible and Sintered Glass Crucible
Material Composition
The primary difference between Gooch crucibles and sintered glass crucibles lies in their material composition. Gooch crucibles are typically made from porcelain or ceramic, offering good thermal resistance. On the other hand, sintered glass crucibles are made from borosilicate glass, providing excellent chemical resistance and transparency.
Porosity and Filtration
Gooch crucibles feature a perforated bottom, allowing for efficient filtration. However, the porosity is lower compared to sintered glass crucibles. Sintered glass crucibles have a highly porous structure that provides enhanced filtration capabilities, making them suitable for fine particle separation.
Temperature Resistance
Due to their ceramic or porcelain composition, Gooch crucibles offer higher temperature resistance compared to sintered glass crucibles. Gooch crucibles can withstand high temperatures required for various analytical processes, whereas sintered glass crucibles have lower temperature limits.
Chemical Compatibility
Sintered glass crucibles have superior chemical resistance compared to Gooch crucibles. The borosilicate glass used in sintered glass crucibles can withstand a wide range of acids, bases, and organic solvents. Gooch crucibles, although resistant to many chemicals, may not be suitable for certain corrosive substances.
Frequently Asked Questions
Up to 1600°C.
No, they are too fragile and porous.
Gooch is porous for filtrations, and sintered glass is non-porous.
No, it cannot filter solutions.
Sintered glass.
Conclusion – Gooch crucible vs Sintered glass
In summary, Gooch crucibles are best suited for lower-temperature filtrations while sintered glass crucibles excel at high-temperature applications requiring chemical resistance and reuse. Consider the specific needs of the application when deciding between these two important types of chemistry lab crucibles. Both Gooch and sintered glass crucibles serve critical roles in gravimetric analysis, ignitions, fusions, and other essential laboratory techniques.
Also, read another post Difference Between p Alkalinity and m Alkalinity in water
Reference links